No products in the cart.
Chess Tournaments
FIDE Grand Prix: Elite Chess Tournaments for Top Players in the World
The FIDE Grand Prix is a prestigious series of elite chess tournaments featuring top players from around the world. Organized by the Fédération Internationale des Échecs (FIDE), the governing body of international chess, the FIDE Grand Prix offers a platform for elite chess players to compete against each other in a series of tournaments held in different locations across the globe. The tournaments are known for their high level of competition, with top players vying for coveted Grand Prix points to qualify for the Candidates Tournament, which determines the challenger for the World Chess Championship title. In this article, we will delve into the details of the FIDE Grand Prix, its format, significance, and impact on the chess world, highlighting the excitement and prestige associated with these top-tier chess competitions.
Table of Contents
History and Evolution of FIDE Grand Prix
The FIDE Grand Prix has a rich history that spans over a decade, with its evolution reflecting the changes and developments in the world of chess. The concept of the FIDE Grand Prix originated as part of FIDE’s efforts to revamp the World Chess Championship cycle and create a more transparent and competitive system.
The first FIDE Grand Prix cycle was launched in 2008 and consisted of six tournaments held in various cities around the world. Over the years, the format and schedule of the FIDE Grand Prix have evolved. In some cycles, the number of tournaments and participants varied, and the format changed to a knockout system where players faced off in matches instead of round-robin events. The locations of the tournaments have also varied, with cities from different regions around the world hosting the FIDE Grand Prix, providing opportunities for chess fans from different countries to witness the top-level competition. The FIDE Grand Prix has witnessed remarkable performances from some of the world’s best chess players, with players showcasing their skills, strategies, and creativity on the chessboard.
The FIDE Grand Prix has undergone changes and adaptations over the years, reflecting the evolving landscape of chess and the desire to create a competitive and transparent system for determining the World Chess Championship challenger. It has become a significant part of the chess world, providing opportunities for players to showcase their skills, earn accolades, and vie for the prestigious title of World Chess Champion.
Format of FIDE Grand Prix Tournaments
The format of FIDE Grand Prix tournaments has evolved over the years, with different cycles featuring varying structures. The format for each cycle is determined by FIDE, the international governing body for chess, and may be subject to changes from cycle to cycle.
Typically, FIDE Grand Prix tournaments feature a round-robin format, where a group of top chess players from around the world compete against each other. The exact number of players and rounds may vary depending on the cycle, but it is common to have around 16 players competing in each tournament. The players face each other once, with games played at a time control determined by FIDE.
The players are selected based on various criteria, including their FIDE ratings, previous performance in FIDE events, and other qualification paths, as determined by FIDE’s regulations for the specific cycle. The participants in the FIDE Grand Prix tournaments are typically some of the world’s highest-ranked chess players, including current and former World Chess Champions, top-rated players, and other accomplished grandmasters.
The winner of each FIDE Grand Prix tournament earns a predetermined number of Grand Prix points, depending on their final standing. The accumulation of Grand Prix points across the tournaments in a cycle determines the overall standings and the player with the highest total Grand Prix points at the end of the cycle qualifies for the Candidates Tournament, which is the final step in determining the challenger for the World Chess Championship title.
In some cycles, the format of the FIDE Grand Prix has also included knockout stages, where players face off in matches instead of round-robin events. The knockout format typically involves head-to-head matches between pairs of players, with winners advancing to the next round and losers being eliminated until a final winner is determined.
The time controls for FIDE Grand Prix tournaments are typically in line with FIDE’s standard time control regulations, which may vary depending on the cycle and the specific event. FIDE’s time controls specify the amount of time each player has to make their moves during the game, and may also include increment or delay rules to ensure a fair and competitive playing environment.
The format of FIDE Grand Prix tournaments is carefully designed to provide a competitive and fair playing environment for the top players in the world, with the goal of determining the challenger for the World Chess Championship title. It offers an exciting and challenging competition for chess players and fans alike, showcasing the highest level of chess skill, strategy, and creativity on the global stage
Prize Funds and Sponsorship for FIDE Grand Prix
The prize fund for FIDE Grand Prix tournaments typically consists of an amount of money, which is divided among the top finishers based on their final standings. In addition to the prize funds, FIDE Grand Prix tournaments may also receive sponsorship in the form of financial support, in-kind contributions, or other benefits from sponsors. Sponsors may provide funding to cover various expenses associated with organizing the tournaments, such as venue costs, equipment, travel, accommodation, and other logistical needs. Sponsors may also contribute to the overall prize fund, increasing the attractiveness of the tournaments for top players and helping to elevate the level of competition. Sponsorship for FIDE Grand Prix tournaments can come from a variety of sources, including corporate sponsors, governments, chess organizations, philanthropic foundations, and other entities interested in supporting the advancement of chess and promoting the sport on a global scale.
The availability and size of the prize funds and sponsorship for FIDE Grand Prix tournaments can vary on various factors, such as the overall economic climate, the level of interest and investment in chess, and the specific cycle and event. FIDE actively seeks sponsors to support the organization and implementation of the FIDE Grand Prix tournaments, with the goal of providing a high-quality and rewarding experience for the players while promoting the sport of chess worldwide.
Notable Players and Champions in FIDE Grand Prix
Many renowned chess players and champions have participated in the FIDE Grand Prix tournaments over the years, adding prestige and excitement to these events. These players have demonstrated exceptional talent, strategic prowess, and tactical acumen on the chessboard, making them formidable contenders in the tournament.
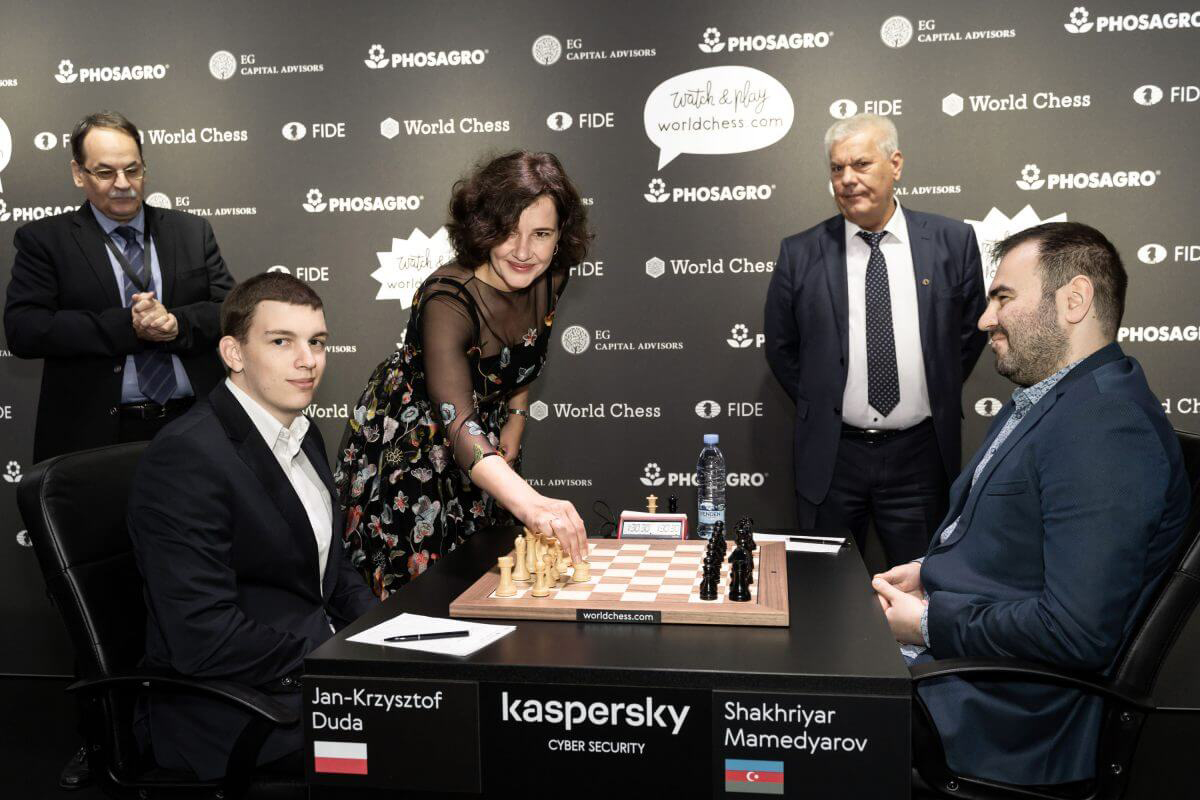
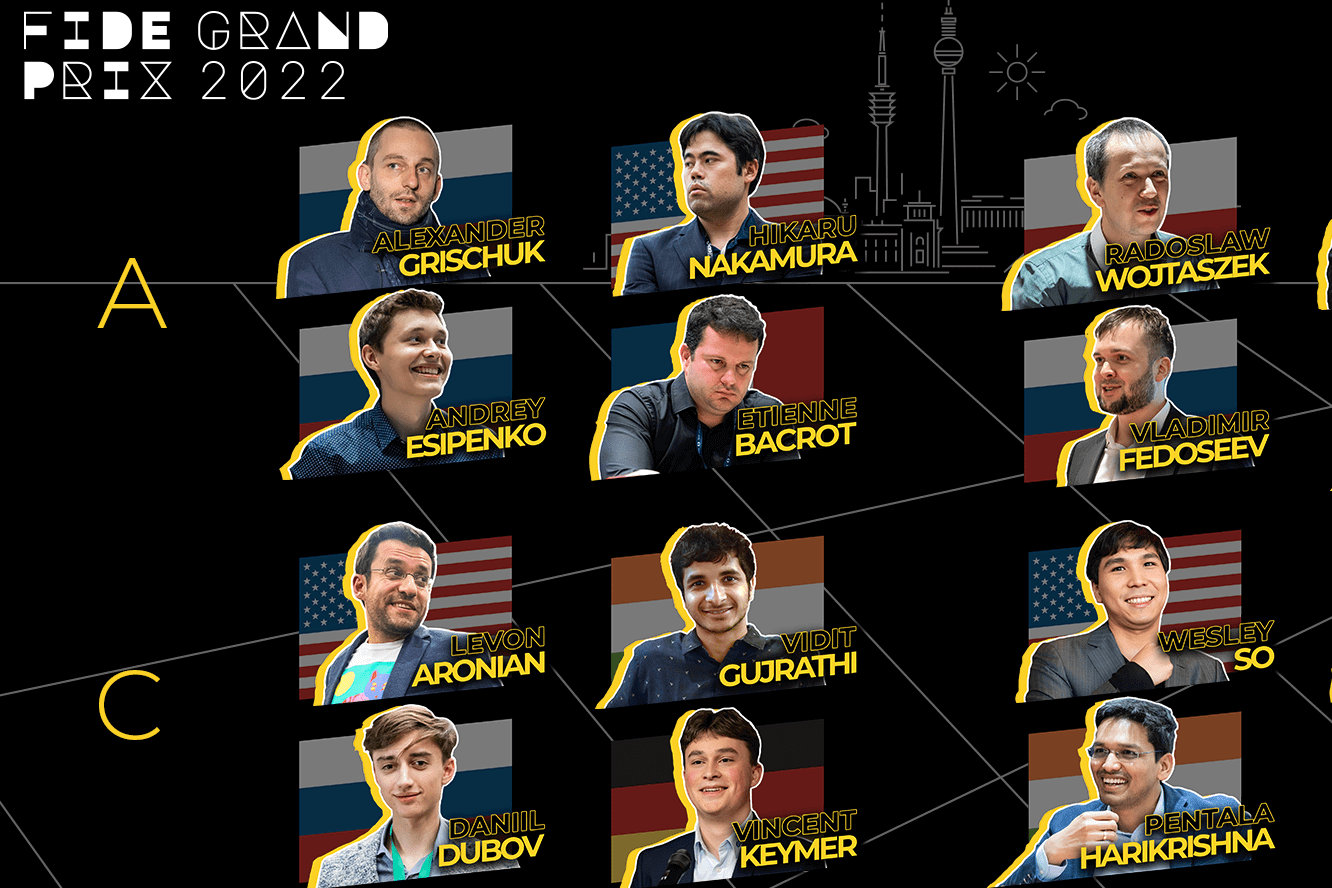
Some notable players who have participated in the FIDE Grand Prix tournaments include former World Chess Champions such as Viswanathan Anand, Vladimir Kramnik, Veselin Topalov, and Rustam Kasimdzhanov. These players have had illustrious careers and have left an indelible mark on the chess world with their achievements and contributions to the game. In addition to the former World Chess Champions, other top-rated players such as Fabiano Caruana, Hikaru Nakamura, Wesley So, Shakhriyar Mamedyarov, Levon Aronian, and Maxime Vachier-Lagrave, among others, have also competed in the FIDE Grand Prix tournaments. These players are known for their exceptional skills, dedication to the game, and consistent performances in elite chess competitions.
Furthermore, the FIDE Grand Prix tournaments have also provided a platform for emerging talents and rising stars in the chess world to showcase their potential and compete against established players. Many young and talented players have participated in the FIDE Grand Prix tournaments and have made a name for themselves with their impressive performances and breakthroughs in these high-profile events.